Geometries
Each of the physics bodies covered in the previous section require you to attach some kind of geometry to them which will define their geometry in the physics engine.
Remember that the physics engine only “sees” these geometries, and will detect collision of your physics bodies by checking for overlap between these geometries.
The geometry of your physics body can be a box, a plane, a sphere, a capsule, a cylinder, or a collision geometry.
To add one to your entity, add its corresponding geometry component (i.e.
Box
Compatible with: static body, rigid body, kinematic rigid body, character controller
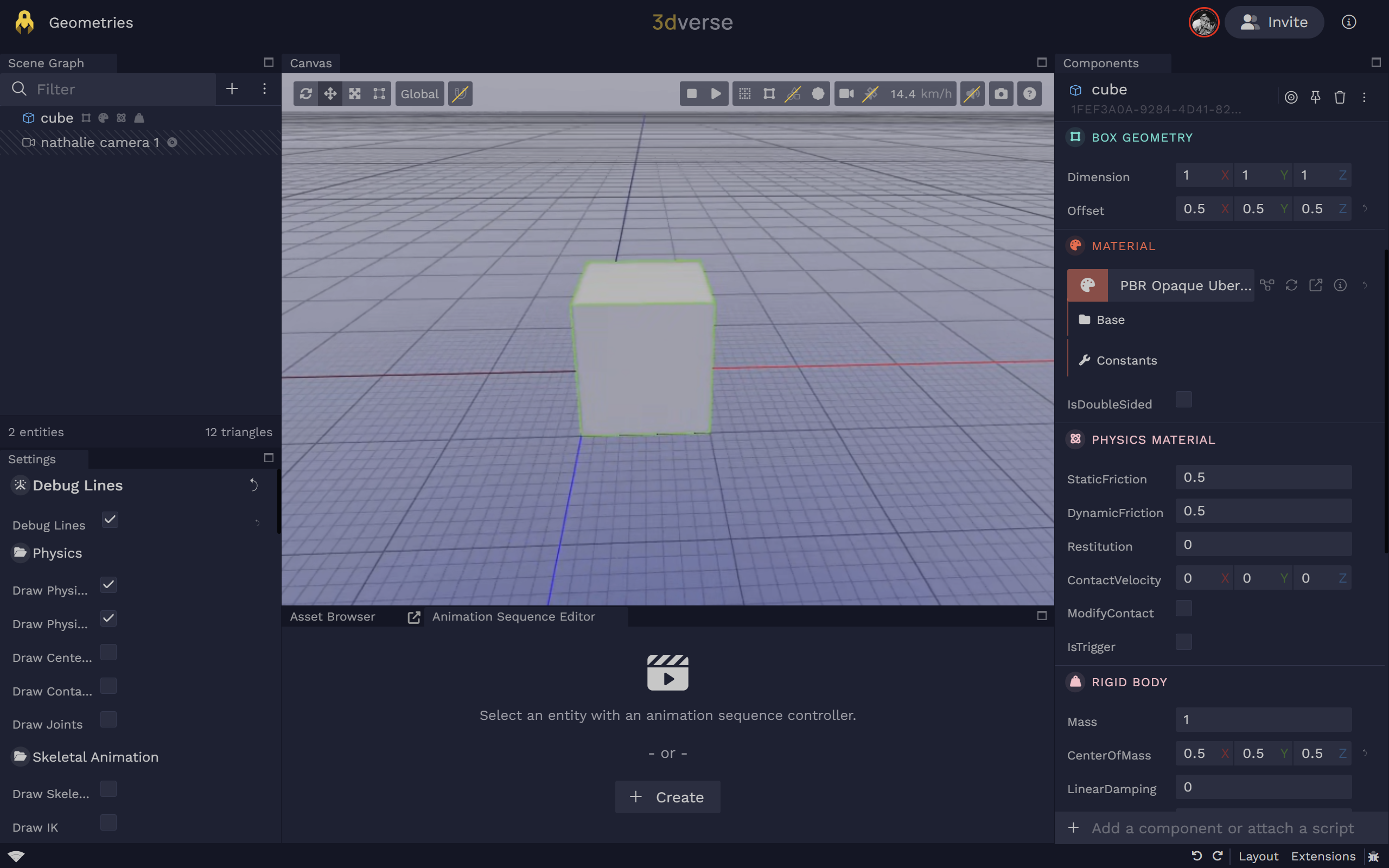
Box Geometry
box_geometry
Box geometry.
Box Geometry
box_geometry
Box geometry.
dimension
Vector3(m)
Default:[1,1,1]
Box dimensions (width, height, depth) in meters.
Box dimensions (width, height, depth) in meters.
offset
Vector3(m)
Default:[0,0,0]
Local offset of the geometry origin (meters).
Local offset of the geometry origin (meters).
Plane
Compatible with: static body, kinematic rigid body
Planes divide space into "above" and "below" them. Everything "below" the plane will collide with it.
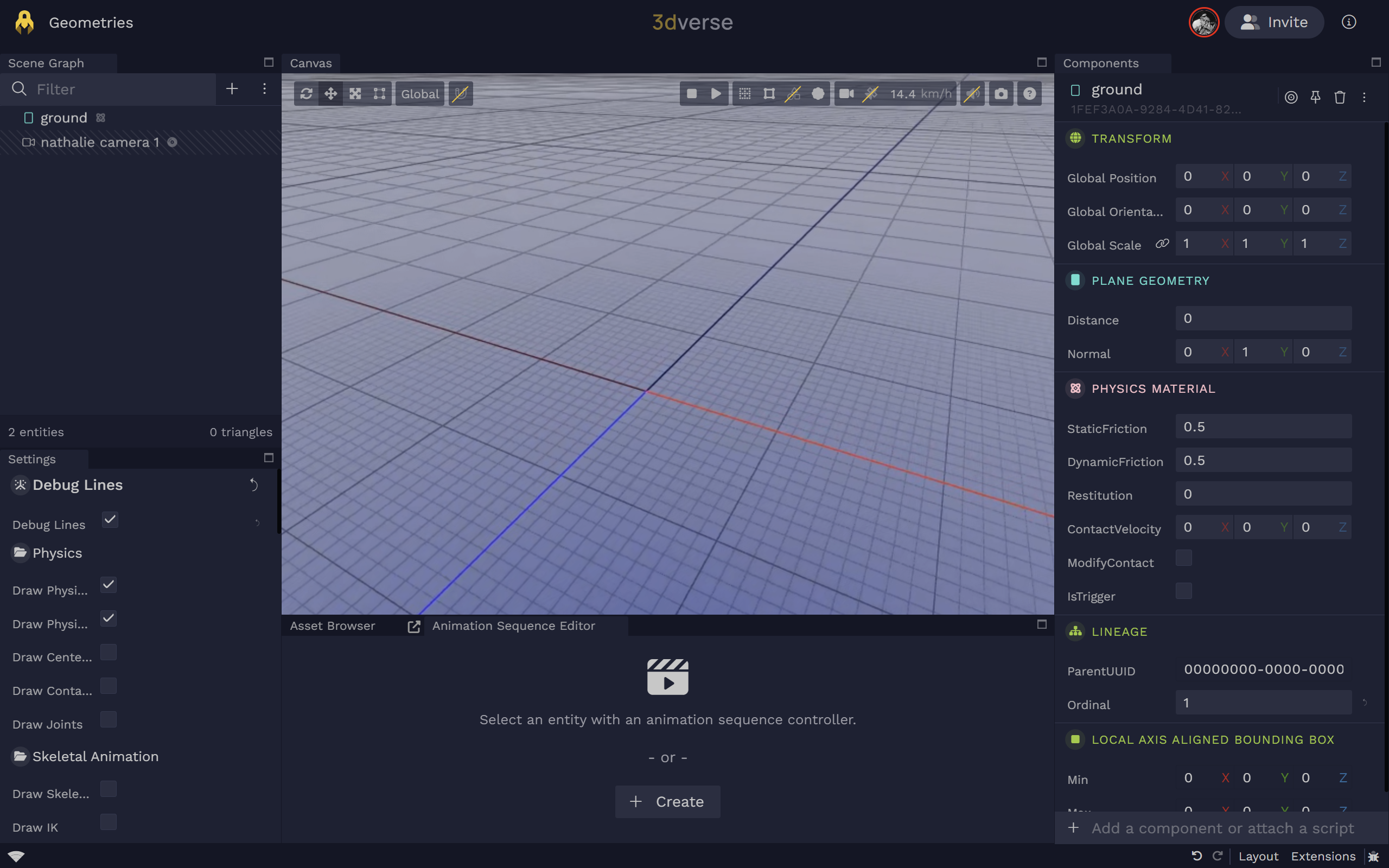
Plane Geometry
plane_geometry
Infinite plane geometry.
Plane Geometry
plane_geometry
Infinite plane geometry.
distance
Float(m)
Default:0
Signed distance from the origin along the plane normal (meters).
Signed distance from the origin along the plane normal (meters).
normal
Vector3
Default:[0,1,0]
Unit normal vector of the plane (in local space).
Unit normal vector of the plane (in local space).
Sphere
Compatible with: static body, rigid body, kinematic rigid body
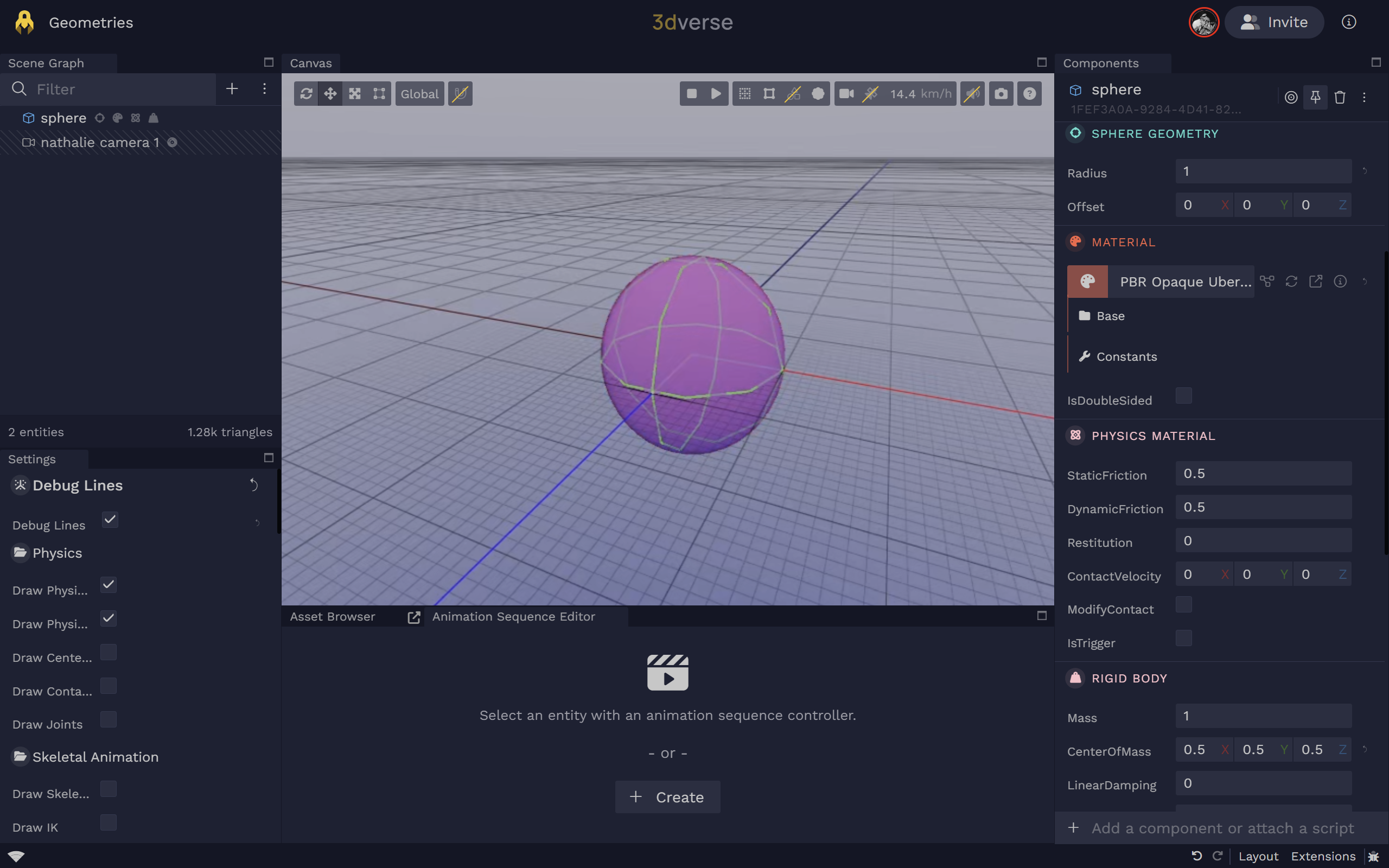
Sphere Geometry
sphere_geometry
Sphere geometry.
Sphere Geometry
sphere_geometry
Sphere geometry.
offset
Vector3(m)
Default:[0,0,0]
Local offset of the geometry origin (meters).
Local offset of the geometry origin (meters).
radius
Float(m)
Default:0.5
Radius of the sphere (meters).
Radius of the sphere (meters).
Cylinder
Compatible with: static body, rigid body, kinematic rigid body
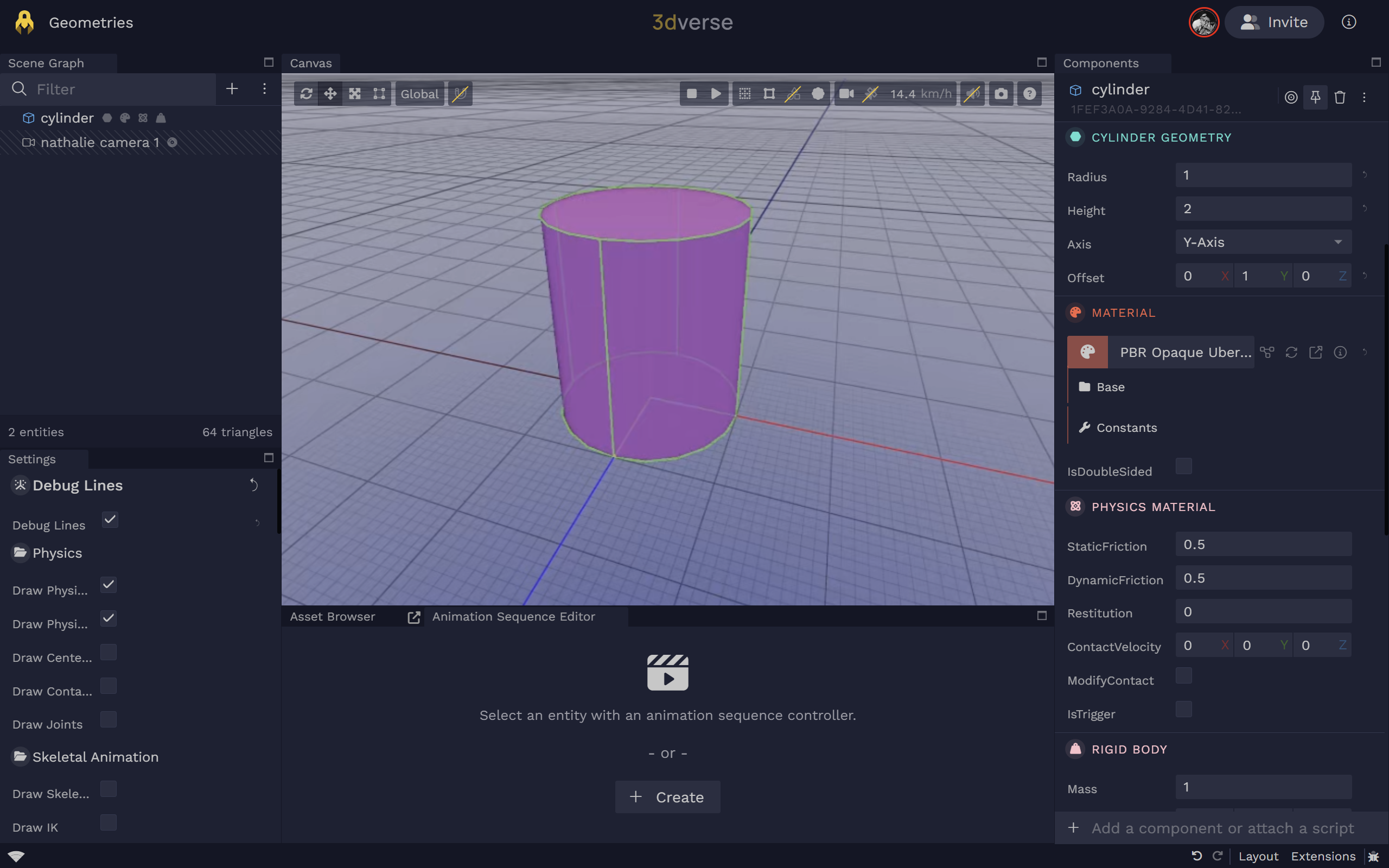
Cylinder Geometry
cylinder_geometry
Cylinder geometry.
Cylinder Geometry
cylinder_geometry
Cylinder geometry.
axis
Integer
Default:1(Y-Axis)
Alignment axis of the cylinder: 0=X, 1=Y, 2=Z.
0X-Axis1Y-Axis2Z-Axis
Alignment axis of the cylinder: 0=X, 1=Y, 2=Z.
height
Float(m)
Default:1
Height of the cylinder (meters).
Height of the cylinder (meters).
offset
Vector3(m)
Default:[0,0,0]
Local offset of the geometry origin (meters).
Local offset of the geometry origin (meters).
radius
Float(m)
Default:0.5
Radius of the cylinder (meters).
Radius of the cylinder (meters).
Capsule
Compatible with: static body, rigid body, kinematic rigid body, character controller
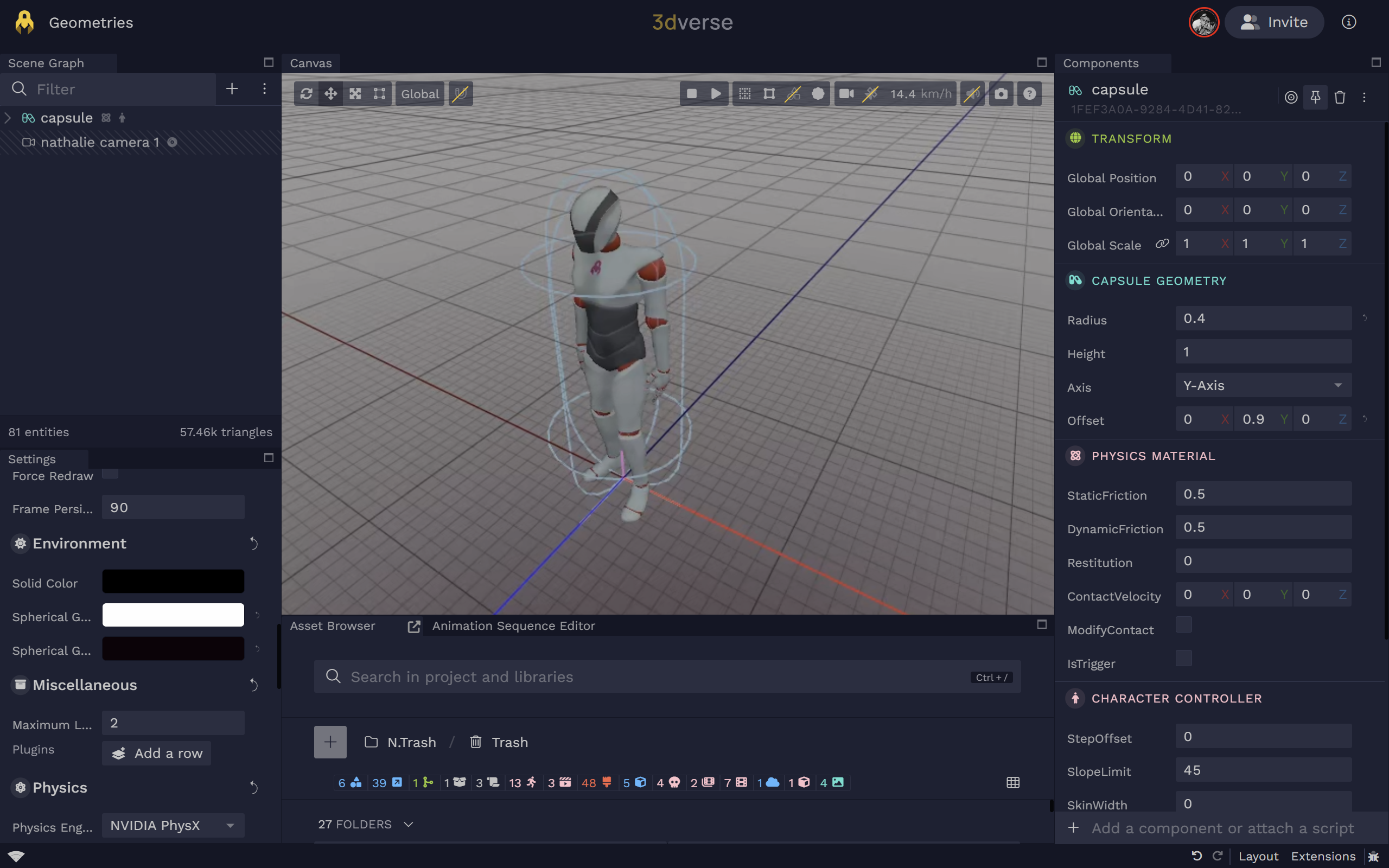
Capsule Geometry
capsule_geometry
Capsule geometry.
Capsule Geometry
capsule_geometry
Capsule geometry.
axis
Integer
Default:1(Y-Axis)
Alignment axis of the capsule: 0=X, 1=Y, 2=Z.
0X-Axis1Y-Axis2Z-Axis
Alignment axis of the capsule: 0=X, 1=Y, 2=Z.
height
Float(m)
Default:1
Height of the cylindrical mid-section (meters).
Height of the cylindrical mid-section (meters).
offset
Vector3(m)
Default:[0,0,0]
Local offset of the geometry origin (meters).
Local offset of the geometry origin (meters).
radius
Float(m)
Default:0.5
Radius of the hemispherical ends (meters).
Radius of the hemispherical ends (meters).
Collision Geometry
Compatible with: Read below
collisionGeometryRef
Referenced collision geometry (UUID).
Referenced collision geometry (UUID).
If you want to use a triangular mesh or a convex mesh as a geometry for your physics body, you need to create a collision geometry. A
There are two types of collision geometry:
Convex
- This is a convex mesh, that will encapsulate all the points of your mesh. A mesh is convex if, given any two points within it, the mesh contains the line between them.
- Compatible with: static body, rigid body, kinematic rigid body
Triangular
- This is a triangular mesh, that will encapsulate all the points of your mesh. It will wrap as closely to the original mesh you provide as possible.
- Compatible with: static body, kinematic rigid body
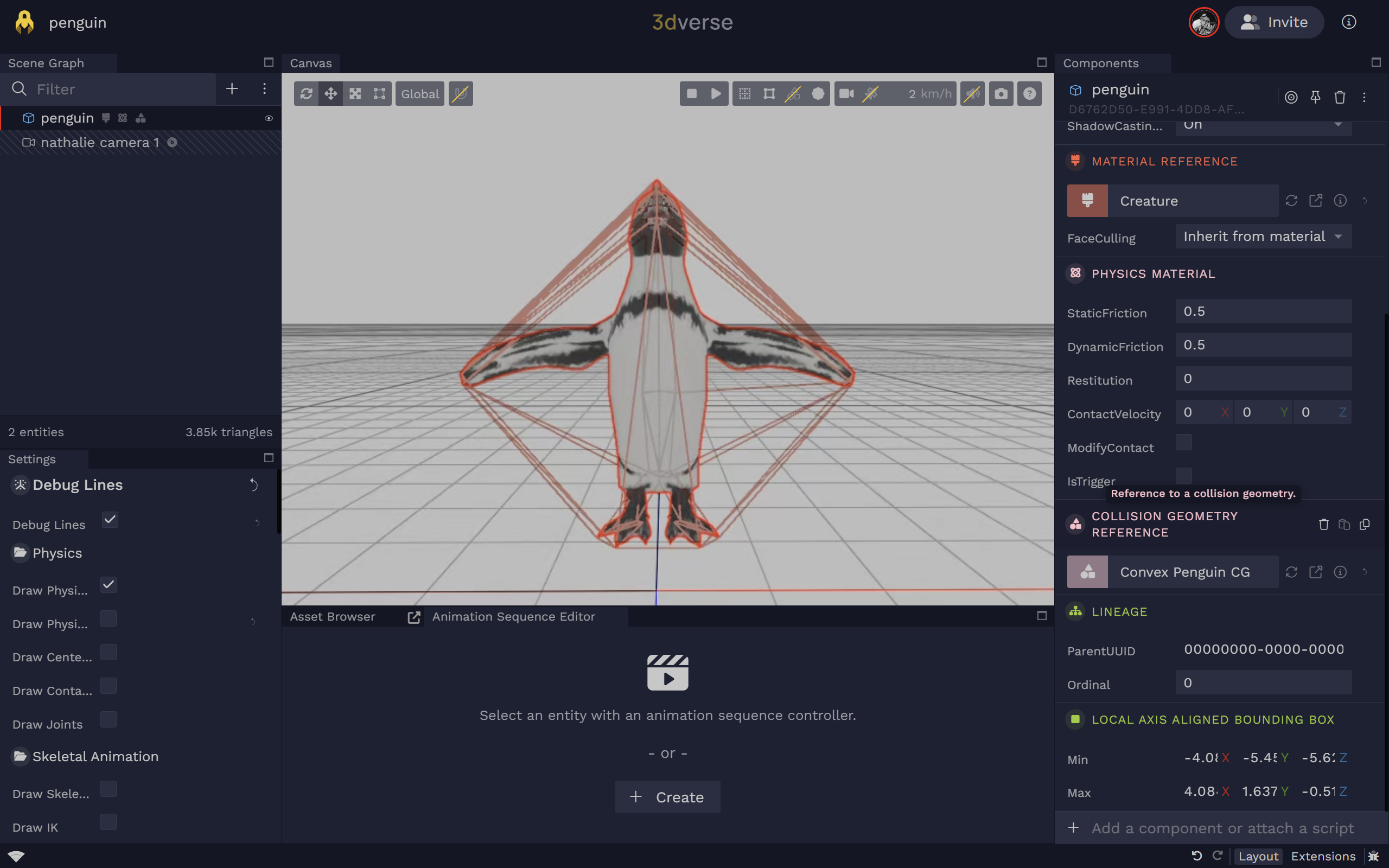
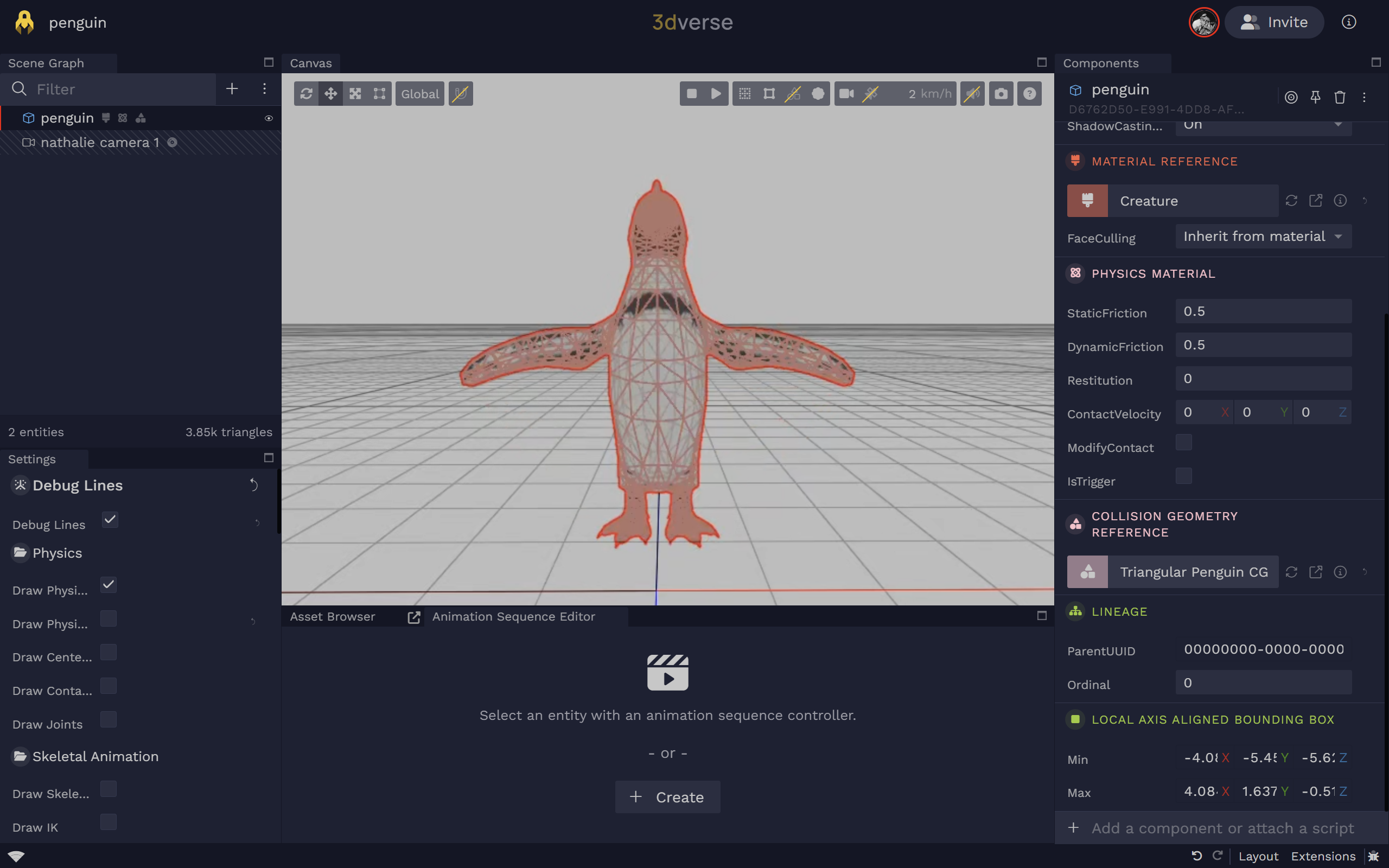
Between the two, the convex collision geometry is the recommended default choice. A convex collision geometry is less computationally heavy as it contains less vertices than the triangular collision geometry. Also, triangular collision geometries cannot be assigned to rigid bodies.
To create a collision geometry, right click on an entity with a mesh reference component in your scene graph and select Create convex collision geometry
or Create triangular collision geometry
.
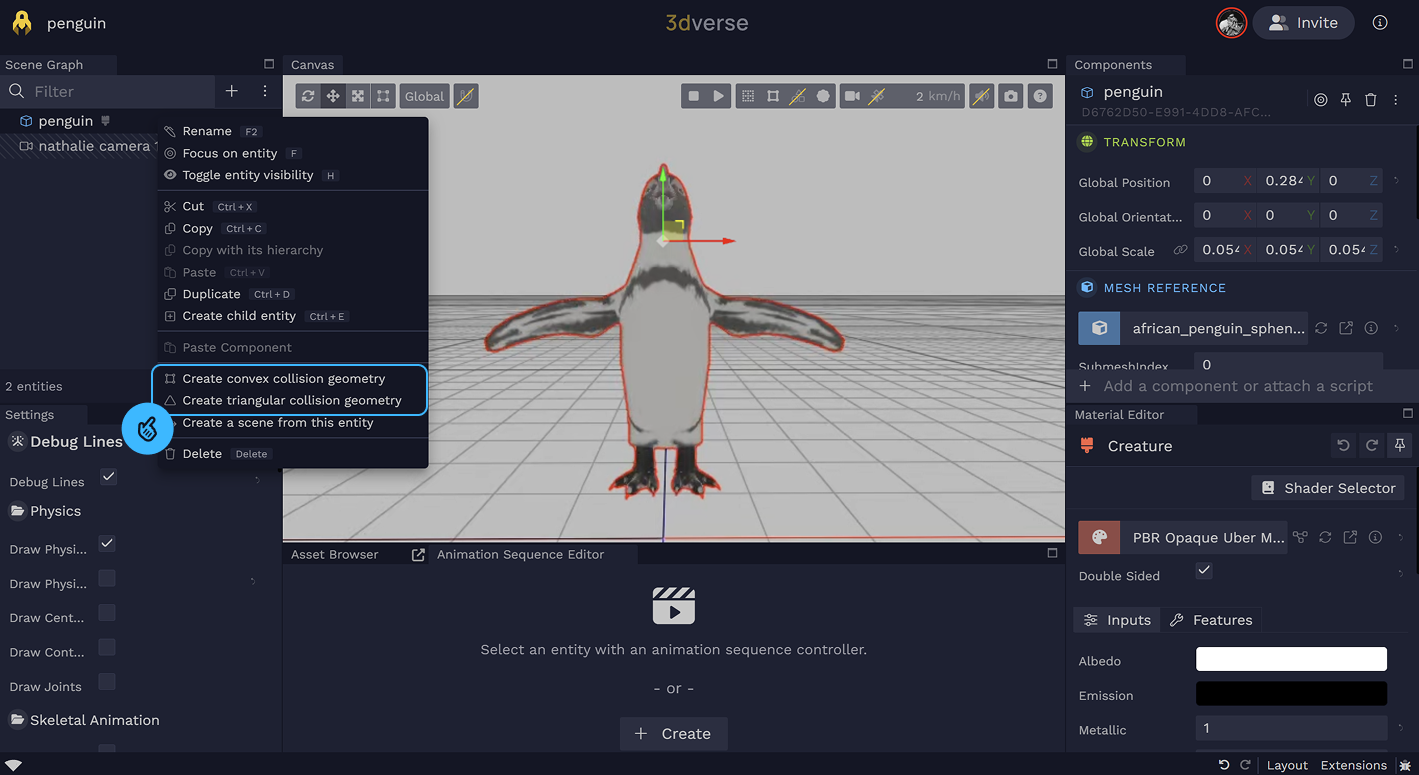
Once the collision geometry is created, your entity will be automatically assigned a collision geometry reference component and the collision geometry will be attached to it.